Everything You Need To Know About Eczema
Everything you need to know about eczema
A skin condition in which the skin becomes dry, itchy, red, inflamed, rough, and cracked is known as eczema. In some cases, eczema also causes blisters on the skin. Originating from the Greek word “ekzein”, which means “to boil”, eczema is a condition of dry skin. Almost 31.6% of Americans are affected by this skin condition. Although the exact cause of this condition is still in the dark, doctors and experts believe eczema results from a complex interplay of environmental and hereditary factors.
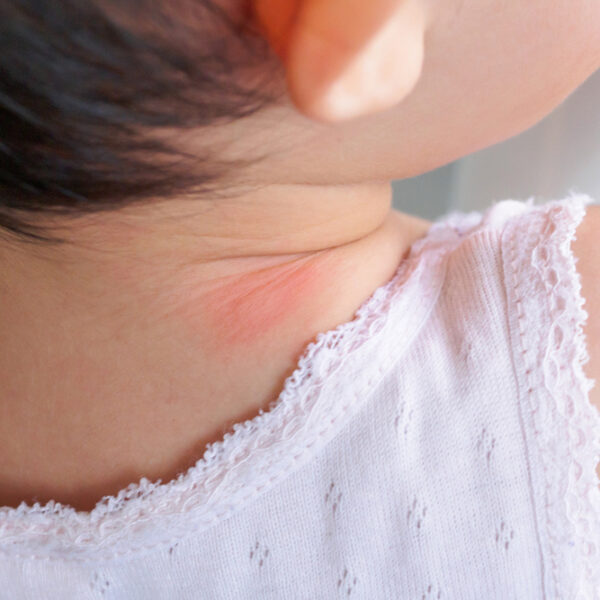

Below is some information to help you understand this skin condition better.
Which are the 7 types of eczema?
- Atopic eczema – Atopic eczema, commonly known as atopic dermatitis or just eczema, is the most common form of eczema. Common causes of atopic eczema are genetics, a problem in the immune system, environmental triggers, and dry skin.
- Contact dermatitis – As the name suggests, contact dermatitis is caused by an allergic reaction to coming in contact with certain elements or substances. Although non-contagious or life-threatening, the rash caused by this type of eczema causes a lot of discomfort.
- Dyshidrotic eczema – Also known as dyshidrosis, dyshidrotic eczema affects the palms and soles of the feet with characteristic blisters. Blisters filled with a fluid form on the toes, fingers, soles of the feet, and palms. Sometimes, these blisters can cause pain and/or itch.
- Hand eczema – This eczema affects only the hands. Usually caused by exposure to chemicals, it often affects people work jobs that expose their hands to irritants like hairdressers, cleaners, health care specialists, etc.
- Stasis dermatitis- Stasis dermatitis is the inflammation of the skin caused by a stagnant circulation and affects lower extremities. It is induced by the leaking of fluids from weakened veins into the skin. The leaked fluids lead to swelling, pain, itching, and redness. It also leads to swelling in the legs, especially, after walking.
- Nummular eczema- Nummular eczema causes round, coin-like spots on the skin. The condition derives its name from the Latin word, “nummular” which means a “coin”. The spots caused by this condition vary from one individual to another and look very different from the typical eczema rashes.
- Neurodermatitis – The cause neurodermatitis is unknown although stress is considered to be a major trigger. It is very similar to atopic dermatitis. Neurodermatitis leads to thick and scaly patches on a person’s arms, back of the neck, genitals, bottom of the feet, and back of the hands. These patches itch the most when a person tries to sleep.
What are the symptoms of severe eczema?
- Any of the above types of eczema, when they become severe cause chronic dryness, itching, and cracking of the skin.
- If infected eczema can become a severe problem in everyday life, disturbing sleep, work, and other daily routines.
- In severe eczema, the skin gets lichenified, which means the skin turns leathery and thick.
What are the treatments that are offered for the advanced cases of eczema?
- The approaches are the same as that for typical eczema, but the treatments are more aggressive.
- To keep the skin moist and itch-free a wet dressing is applied. The healthcare personnel apply a topical corticosteroid cream and cover it with wet bandages. In cases where the eczema is spreading one needs expertise, and it is often done in hospitals.
- Exposing to Ultraviolet A or B or a combination of both, called phototherapy, is used in refractory cases.
- New antibiotics are prescriber. These are found to reduce the skin’s inflammation.
- Other medicines tried are topical applications, which are immune response moderators. As they are believed to be cancerogenic the use is limited for a short duration.
- Always use a humidifier and avoid exposure to variations in temperatures and humidity.
- Living with advanced eczema is very stressful; therefore, distressing techniques like hypnosis and biofeedback are also used.
How is the severity of eczema estimated?
- Doctors use two tools to arrive at an objective assessment of the severity of the eczema skin.
- These are the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) and the Severity Scoring Dermatitis Index (SCORAD).
- EASI is determined by the affected area in each of the four regions of upper extremities, neck and head, lower extremities, and the trunk.
- Doctors decide the severity of eczema by the extent of skin that has turned red, water-filled blisters, hardened patches, itchiness, and subjective signs like depression, insomnia, etc.
- 60% weightage is given to the intensity while 20% of the weightage is allotted to each sign.